【ProAV Lab】3minAV#01 - What is Live Streaming?
By Lumens
November 02, 2021 41160

- A Quick Guide to Live Streaming
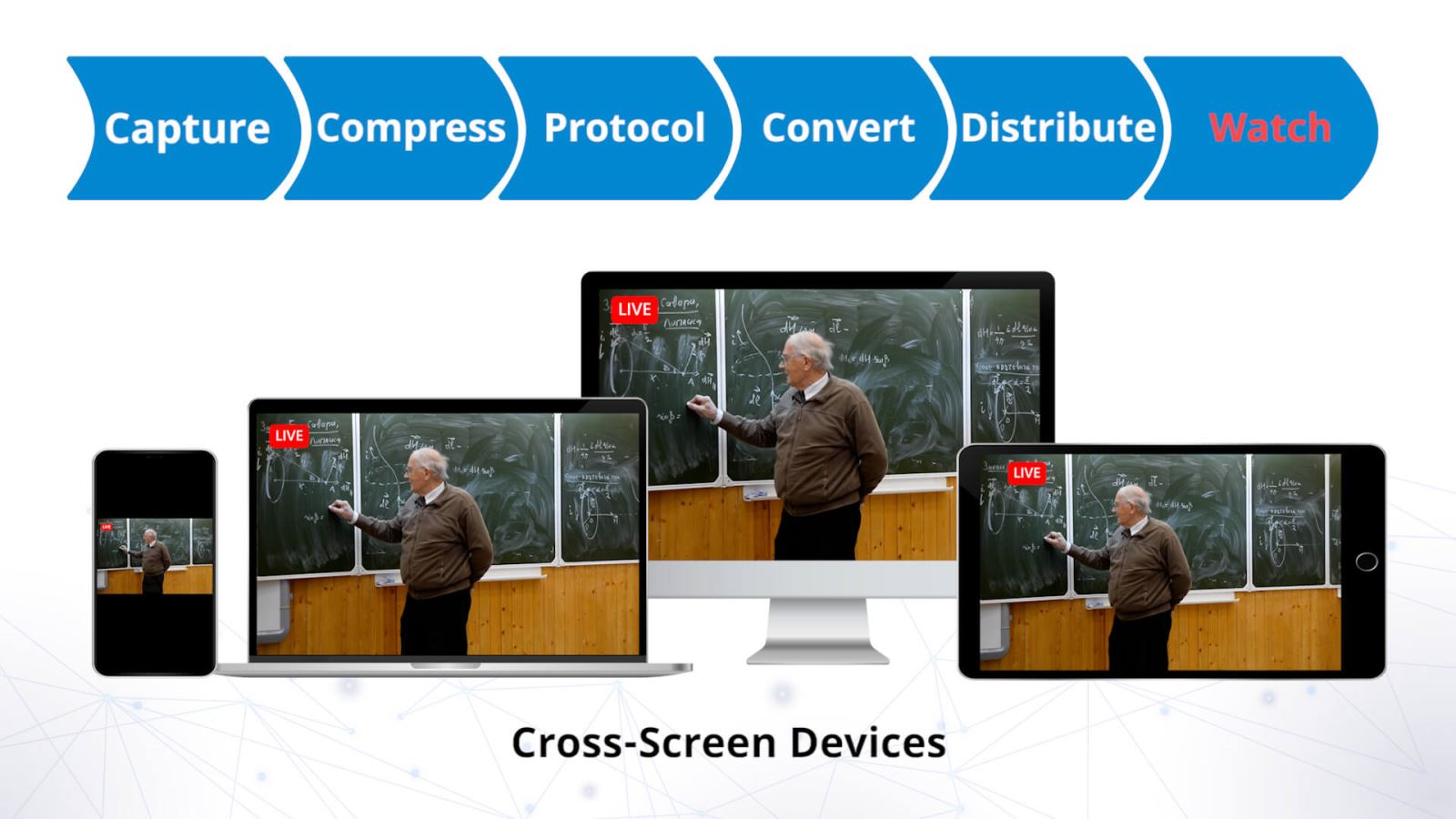
- Step 1: Capture
- Step 2: Compress
- Step 3: Protocol
- Step 4: Convert
- Step 5: Distribute
- Step 6: Watch
- Benefits for Live Streaming
- Live Streaming Challenges
- The Alternative to Live Streaming
With the rapid growth of streaming media, consumers, businesses, worshippers and educators are watching video, TV and events live. With live streaming, viewers can watch an event live on their smartphones, tablets, smart televisions and computers, rather than having to download it after the event has finished. They can often pause and rewind the video, giving them control over how, where and when to watch the stream.
A Quick Guide to Live Streaming
Here is a short guide about the process of live streaming from the video capture to the video playback. Although many go about streaming unaware of these steps, understanding each element gives professionals the chance to make informed decisions. This will have a positive impact on the quality of the viewing experience, the security of the video and the reliability of the stream.

Step 1: Capture
Here is a short guide about the process of live streaming from the video capture to the video playback. Although many go about streaming unaware of these steps, understanding each element gives professionals the chance to make informed decisions. This will have a positive impact on the quality of the viewing experience, the security of the video and the reliability of the stream.

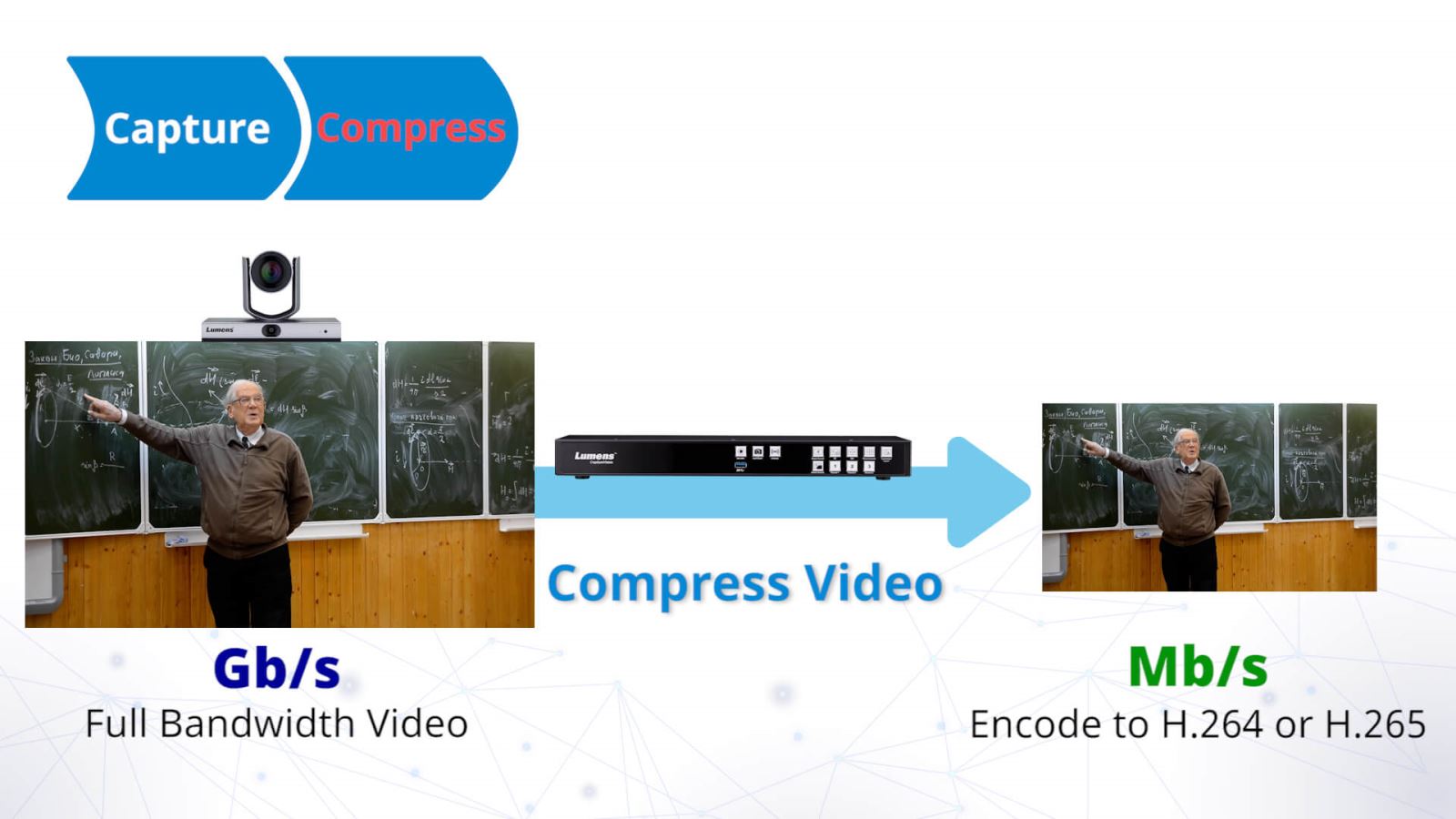
Step 2: Compress
Using a dedicated media processor, the video coming from the camera is compressed into a manageable size. By adopting a standard such as H.264, file sizes are small, but the picture quality is high. Opting for the newer H.265 halves the data rate again and is fantastic if you're streaming to a network that supports the format. Both H264 and H265 are very efficient, though, meaning that your video is more likely to be free of stutter or glitches when it is streamed to the audience, whether the viewer is on a local network or watching via the Internet. Although a computer can be used to compress the video, users often find that a dedicated hardware processor is easier to manage, is usually more reliable and can be easier to use.
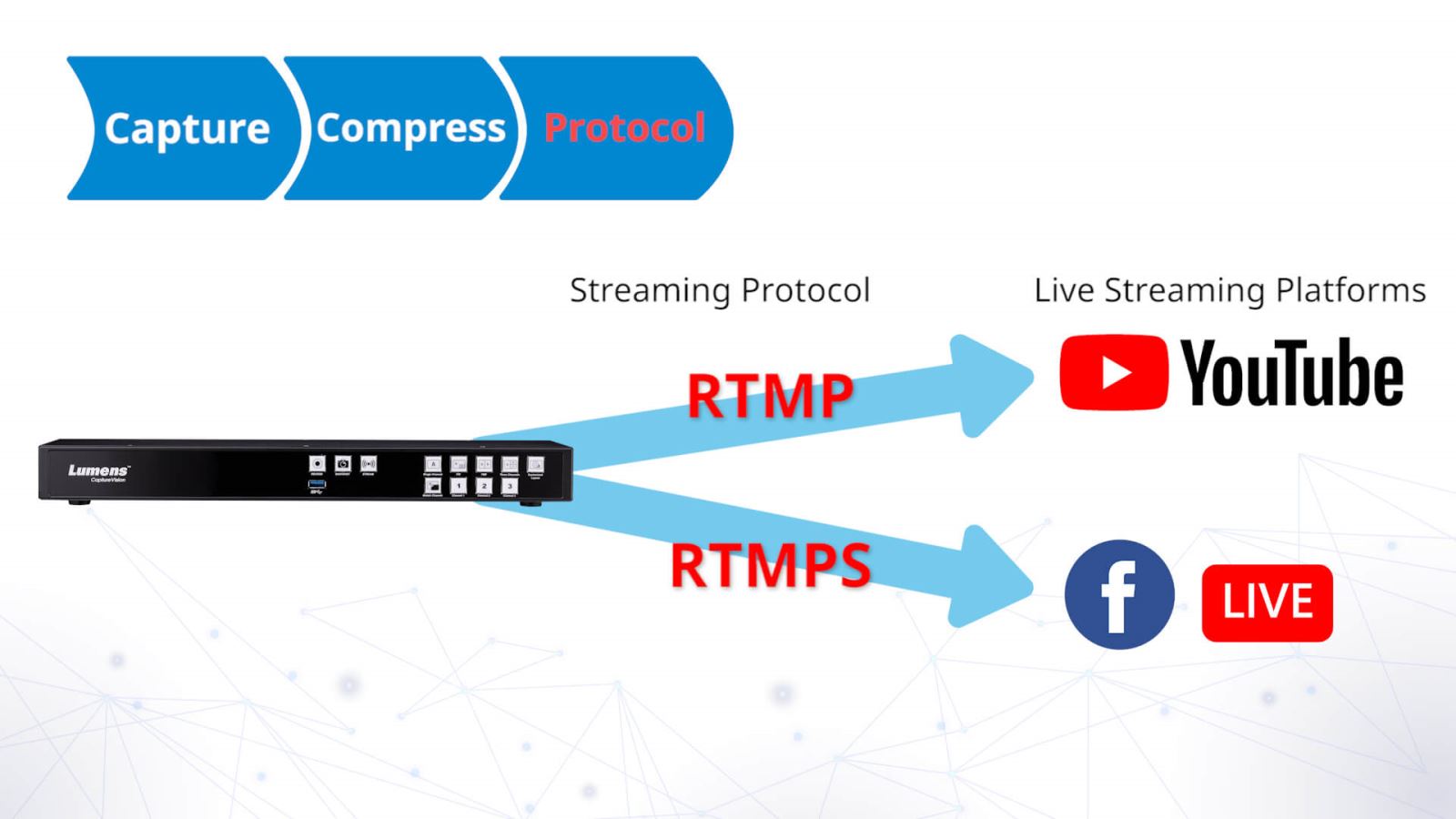
Step 3: Protocol
After the video has been compressed, it is next packaged into a streaming protocol, such as RTMP, RTMPS, SRT or WebRTC, so that the video can be transmitted to the live streaming platform via the Internet.
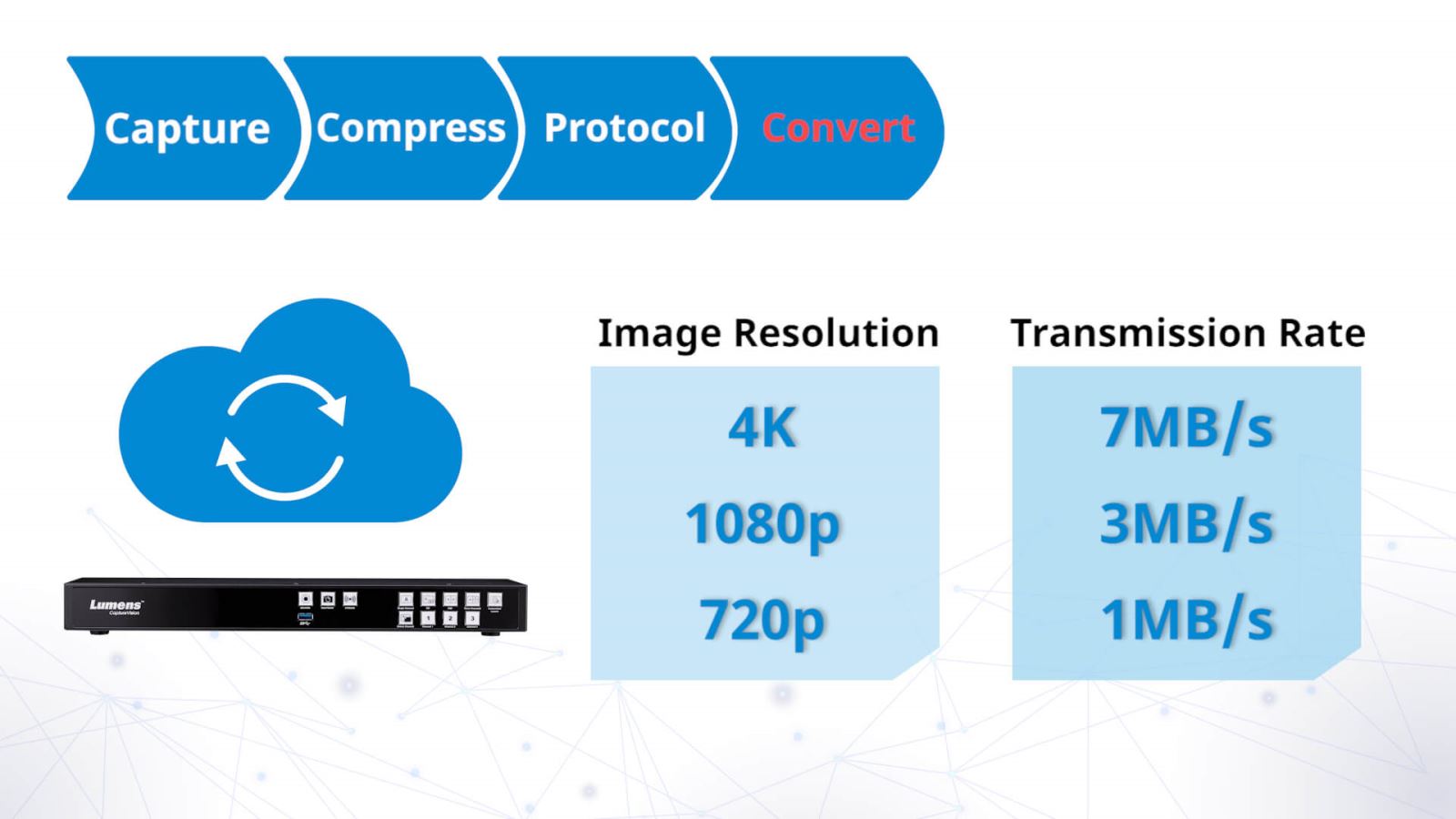
Step 4: Convert
If you are transmitting via a fast network to users on a super-quick broadband or 5G connection, it's possible to stream in 4K. However, if network conditions fluctuate or if the viewer doesn't have an Ultra HD screen, converting a video to HD or even SD (standard definition) might be necessary to keep the transmission smooth. This stage can be performed by the local processor if the transmission network cannot handle high data rates. This is often the case when you're streaming over WiFi, mobile connection or using a shared network. The conversion process can also be managed by the streaming network in the cloud, giving the viewers the option to watch the video in SD, HD or 4K resolution.
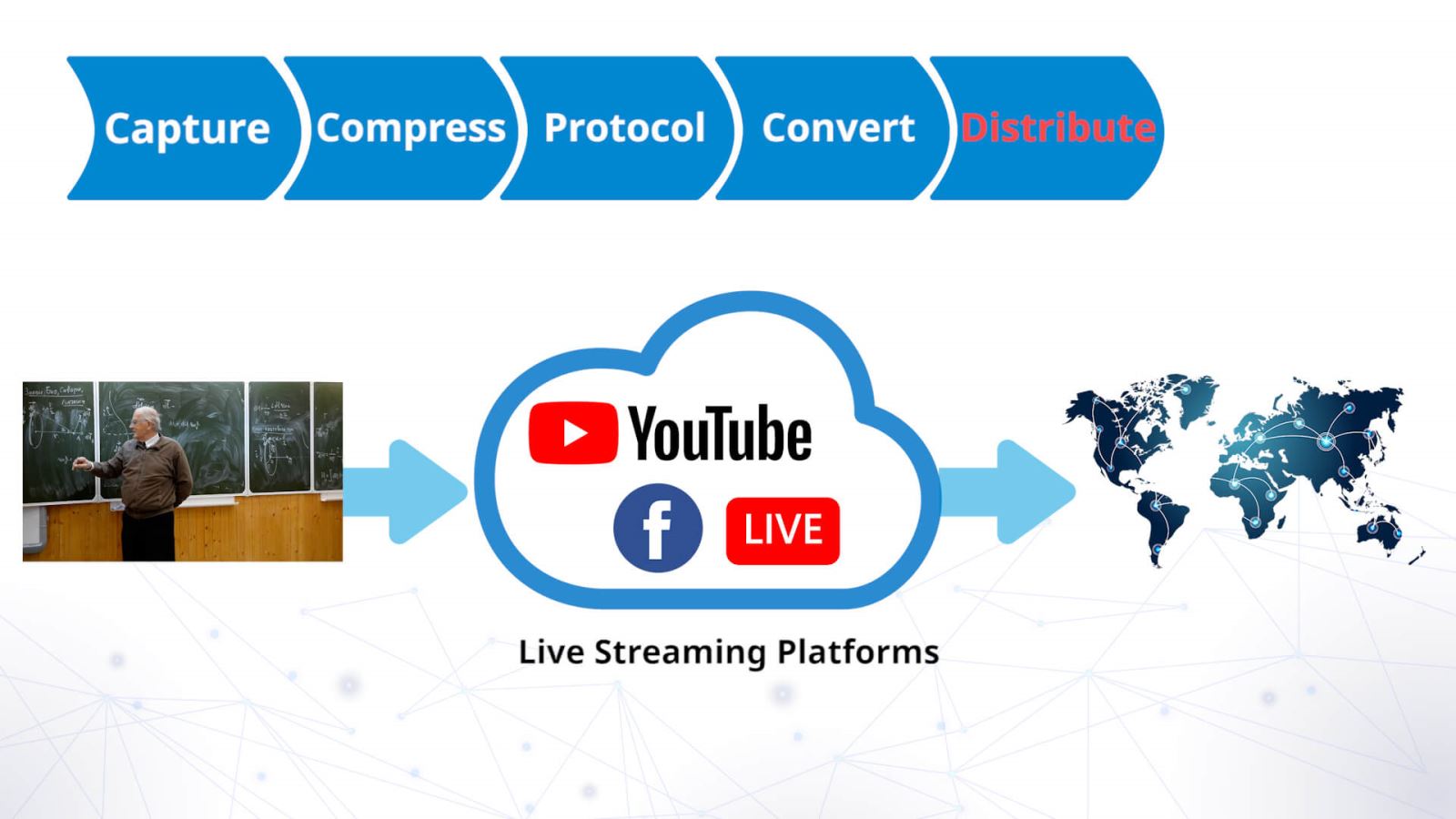
Step 5: Distribute
Viewers watch the live video via a streaming platform such as YouTube or Facebook Live. This means that there is virtually no limit on the size of the audience. Either platform gives producers the ability to stream publicly or to selected viewers. Remember, there are alternative networks and not all streaming platforms are the same. Some offer features such as pay-per-view services, geographical limits to the video stream and multi-language support; some support 4K, some introduce impose advertising onto your stream.
Step 6: Watch
Whenever you're producing and streaming video, think about how the content will be viewed. If most of your audience is watching on a mobile phone screen, keep titles large and consider shooting the video in a vertical format. If your audience is likely to be paying to watch via their Smart Television, it's worth investing to produce the best-looking video, using professional cameras, lighting and switching. But you can rest assured that if you're using a good camera, a professional video processor and a recognized streaming platform, you're giving yourself a very good chance of success.
Benefits for Live Streaming
Thanks to live streaming, now you can have greater engagement with audiences. Speed up your content delivery and reach new market around the world.

Live Streaming Challenges
If you have some issues with live streaming, such as you may face the equipment is suddenly malfunctioning, network congestion either from the host side or viewers side, or outage at your CDN streaming service.

The Alternative to Live Streaming
Don’t worry! You can record the video and make it perfect. And then upload it to video-on-demand platforms like Panopto, Kaltura, YouTube and Facebook. Viewers can watch it anytime, anywhere. They can pause, rewind and review at their leisure.

Introducing the 3-Min AV University
Lumens 3-Min AV University is designed to help audiovisual technicians develop new skills and keep up-to-date with the latest advances in technology. We're starting with the launch of a series of short videos. Each will cover essential workflows, untangle the jargon and show the benefits of new technologies.

